Are you worried if you are choosing the right sample for your assessment validation? Ever wondered how to select the right sample size for your assessment validation activities?
If you’ve answered yes to any of these questions, you’re not alone. Many RTOs struggle with the intricacies of validation assessment, particularly when it comes to determining the ideal sample size.
Today in this blog we will help you learn how to calculate a sample size for validation of assessment. We will provide you with a clear understanding of how it impacts your validation assessments. Let’s get started.
But before we teach you anything it is important to understand,
Why calculating a sample size important for validation assessment
While you might be tempted to assess every single assessment, this isn’t always practical or necessary. A carefully selected sample can provide you with valuable insights into the overall quality of your assessments without overburdening your resources.
Imagine you’re conducting a validation assessment for a new training program. If you were to evaluate every single assessment, you’d be spending a significant amount of time and resources. Instead, by calculating an appropriate sample size, you can focus on a representative group of assessments, ensuring that your validation process is both efficient and effective.
For this reason, you can define sample size for validation assessment.
What is a sample size for validation assessment
Sample size refers to the number of assessments you’ll be evaluating during your validation process.
Benefits of Sample Size Calculation for your validation assessments
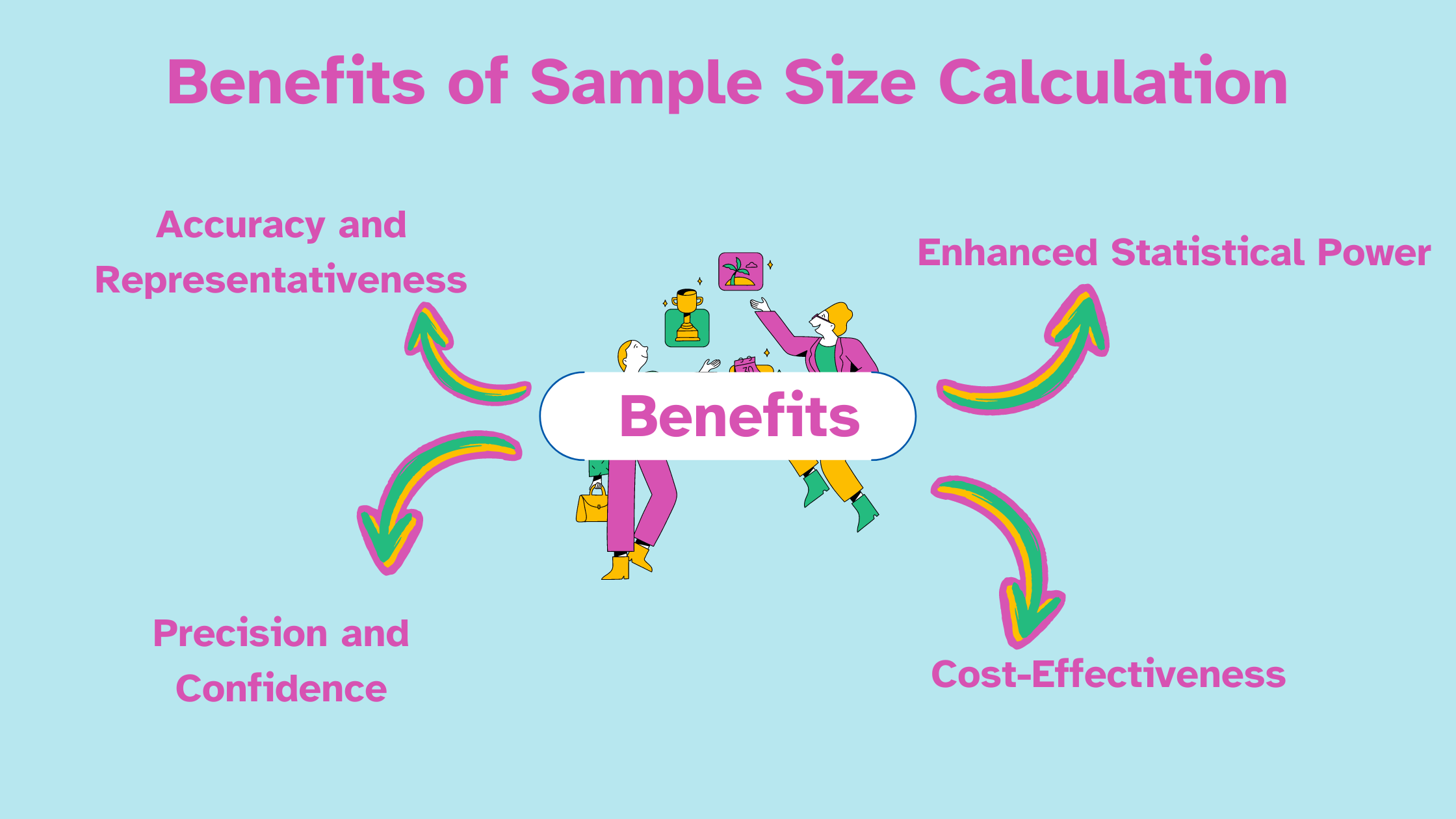
Calculating the right sample size for your validation assessments offers several key advantages:
Accuracy and Representativeness: A well-chosen sample ensures that the assessments you evaluate truly reflect the entire population of assessments. This leads to more accurate and representative results, providing a clearer picture of the overall quality of your assessments.
Enhanced Statistical Power: Statistical power refers to the likelihood of detecting a genuine effect if one exists. A larger sample size bolsters statistical power, reducing the risk of false negatives (concluding that there’s no issue when there actually is).
Precision and Confidence: A larger sample size also allows for more precise estimates of assessment outcomes, filling greater confidence in your findings. This is particularly crucial when making decisions about the quality of your assessments.
Cost-Effectiveness: While a larger sample size might seem counterintuitive, it can actually save you resources in the long run. A poorly selected sample can lead to inaccurate conclusions, requiring further validation efforts and wasting valuable time and money.
What ASQA recommends for Sample Size Calculation for your validation assessments
As an RTO, adhering to ASQA’s guidelines for validation assessments is paramount to maintaining high-quality assessments. ASQA emphasizes the importance of selecting a valid sampling approach that provides sufficient and reliable evidence to ensure your assessments align with the training package requirements, Principles of Assessment, and Rules of Evidence.
While validating every assessment judgement might seem like the safest approach, ASQA recognizes that a well-selected sample can effectively represent the entire set of assessments. To achieve this, ASQA recommends that your sample be:
Large enough: The sample size should be sufficient to ensure that the validation outcomes drawn from the sample can be considered relevant for the entire population of assessments. A larger sample size generally leads to more precise and reliable results.
Random: The sample should be selected randomly from the entire set of assessment judgements being considered. Random selection eliminates bias and ensures that the sample accurately represents the overall assessment population.
Improving Validation with Broad Samples
ASQA specifically recommends that you validate at least two units of competency when validating a qualification, accredited course, or skill set. This broader sample allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of the assessment process across different units of competency. Additionally, you have the flexibility to expand the sample size at any time during the validation process, particularly if the validation outcomes indicate that assessment judgements may not be valid.
How to Select a Random Sample
To select a random sample, ASQA suggests using an alphabetical list of all students who submitted work within the training product being validated. Start by highlighting the fifth surname on the list, and then select every third name thereafter. If you need more records, simply start from the top of the list again using a different number as your starting point.
By following ASQA’s recommendations for sample size calculation and random sample selection, you can ensure that your validation assessments are conducted efficiently, effectively, and in accordance with regulatory requirements. This will empower you to identify areas for improvement and maintain the high quality of your assessments.
Is there an effective way to calculate sample size?
Yes, there is!
ASQA sample size calculator for Sample Size Calculation
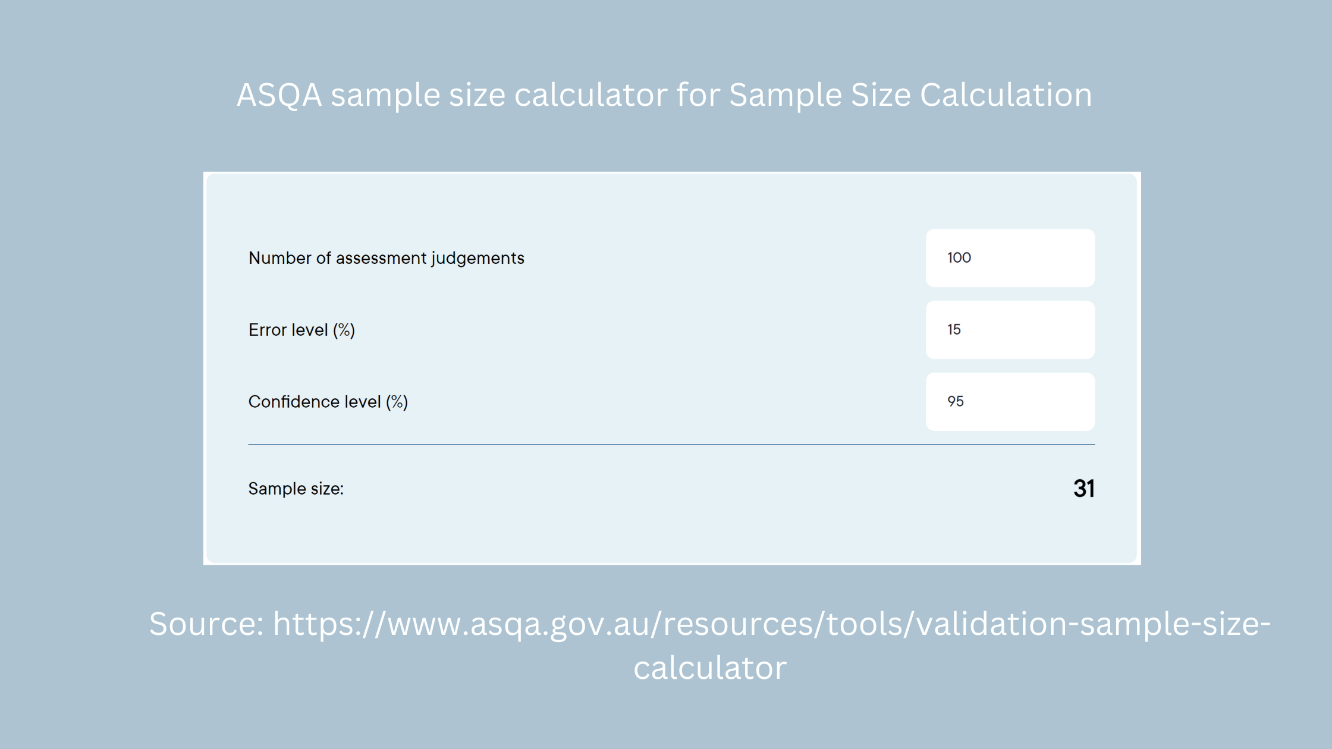
To effectively conduct validation assessments, ASQA has developed a sample size calculator, a tool designed to assist RTOs in determining the appropriate sample size for their validation activities.
Navigating the ASQA Sample Size Calculator
The ASQA sample size calculator requires you to input three key figures:
- Number of assessment judgements: This refers to the total number of assessment judgements made within the training product you are validating during a specific period.
- Error level: The error level, also known as the margin of error, relates to the acceptable range of deviation from the true value. It represents the level of uncertainty you are willing to accept in your sample results.
- Confidence level: The confidence level indicates the degree of certainty you want to have in your sample results. It represents the likelihood that the sample assessment outcomes accurately reflect the overall assessment population.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Sample Size
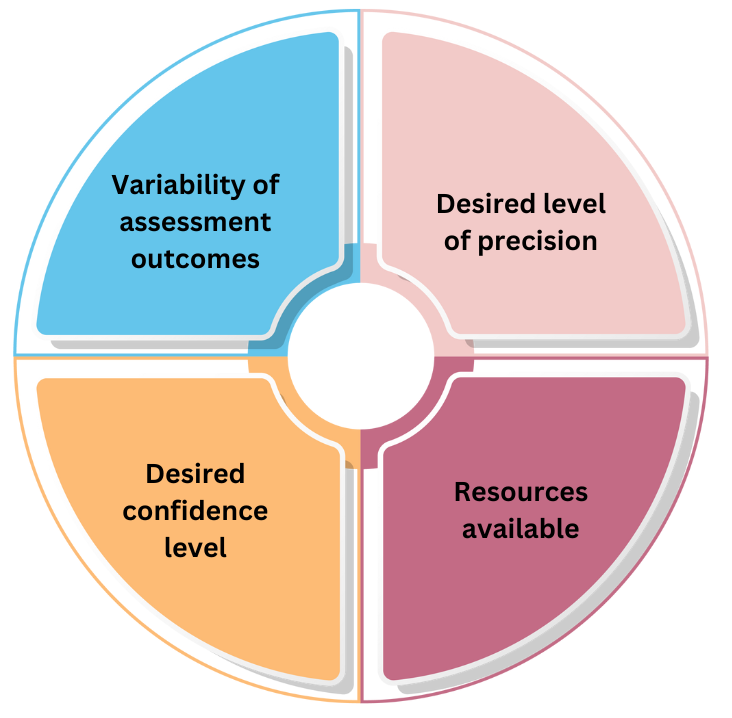
The sample size determined by the calculator is influenced by several factors, including:
- Variability of assessment outcomes: If assessment outcomes are highly variable, a larger sample size will be required to achieve the desired level of precision.
- Desired level of precision: A higher desired level of precision necessitates a larger sample size.
- Desired confidence level: A higher desired confidence level also leads to a larger sample size.
- Resources available: The sample size should be realistic in terms of the resources available for the validation assessment.
Interpreting the Sample Size Result
Once you have entered the required information, the calculator will display the recommended sample size for your validation assessment. This sample size represents the number of assessments you should evaluate to ensure that your validation results are statistically sound and representative of the overall assessment population.
Optimising Validation Efforts with ASQA’s Guidance
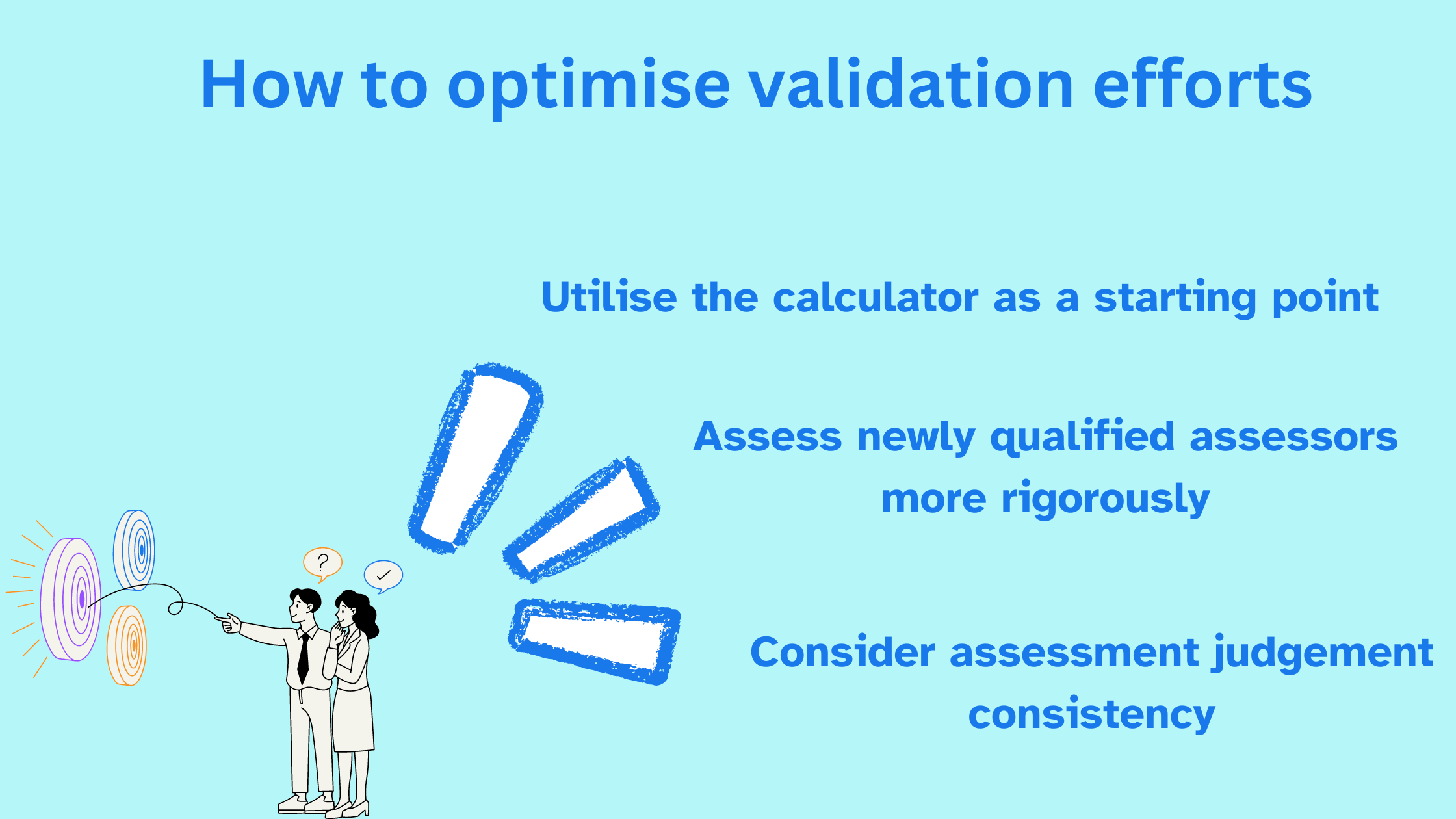
ASQA provides additional guidance to help you make informed decisions about sample size and optimise your validation efforts:
- Consider assessment judgement consistency: If assessment judgements are consistent, a smaller sample size may be sufficient.
- Assess newly qualified assessors more rigorously: When newly qualified assessors are involved, consider increasing the sample size to ensure the accuracy of validation outcomes.
- Utilise the calculator as a starting point: The calculator’s output serves as a starting point for sample size determination. You may need to adjust the sample size based on specific circumstances and risk assessments.
Want guidance in calculating sample size and assessment validation?
At VET Advisory Group we offer assistance and guidance in all matters related to the RTO management and operations. For more information contact us here.
Conclusion
Validation of assessments is a crucial process for RTOs of all sizes. The right sample is definitely a stepping stone for a desirable outcome. Use the information in the blog as a guide for deciding sample size.
A carefully chosen sample, representative of the entire assessment population, can provide valuable insights into the overall quality of your assessments without overburdening your resources.
By understanding the factors influencing sample size, such as the variability of assessment outcomes, desired confidence level, and resources available, you can make informed decisions about the appropriate sample size for your validation assessments.
ASQA’s sample size calculator provides a valuable tool to assist in this process. By inputting the relevant information, you can generate a recommended sample size that aligns with your specific circumstances and regulatory requirements.
Remember, validation assessments are not about evaluating every single assessment. Instead, they are about conducting a comprehensive evaluation of your assessment process to identify areas for improvement and maintain the high quality of your assessments.
So, embrace the power of sample size calculation and empower yourself to conduct effective validation assessments that drive continuous improvement within your RTO.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 critical aspects of validation?
Accuracy, consistency, reliability and relevance.


